Published by K12 Handhelds, Inc.
Portal, AZ
www.k12handhelds.com
Copyright © 2008 by K12 Handhelds, Inc. License CC-by, 
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 United States License.
Developed in conjunction with Wayne Township School System.
Table of Contents
Illustrated Glossary
A-E
acute angle – an angle that is less than 90°
An acute angle is smaller than a perfectly square corner.

acute triangle – a triangle with three acute angles

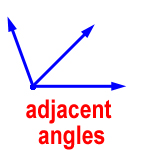
adjacent angles – two angles that share a vertex (the point where two sides meet) and a common side
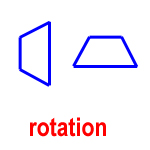
angle of rotation – when rotating a shape, the angle and direction of rotation
The direction is given as clockwise or counter-clockwise.

center of rotation – the fixed point a figure is rotated around
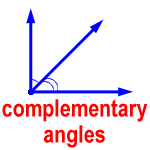
complementary angles – two angles that have a sum of 90°
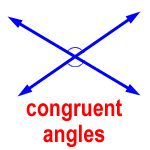
congruent angles – two angles that have the same measurement
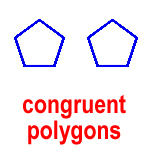
congruent polygons – polygons that have the same shape and the same size
congruent sides – sides that are the same length
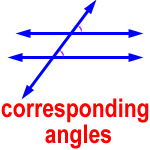
corresponding angles – two congruent angles on the same side of a line that crosses two parallel lines
equilateral triangle – a triangle with three congruent sides

F-Q
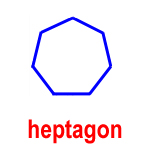
heptagon – a polygon with seven sides
hexagon – a polygon with six sides
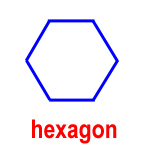
image – the new figure or shape formed after a transformation
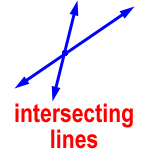
intersecting lines – two lines that meet at a point
isosceles triangle – a triangle with two congruent sides

line of reflection – the line a shape is reflected or flipped over

line of symmetry – the line that divides something with line symmetry
line symmetry – when a figure or shape can be divided by a line so that the part on each side is a mirror image of the part on the other side

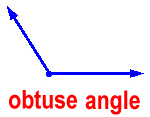
obtuse angle – an angle that is more than 90° but less than 180°
An obtuse angle is bigger than a perfectly square corner, but smaller than a straight line.
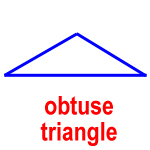
obtuse triangle – a triangle with one obtuse angle
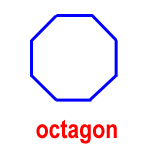
octagon – a polygon with eight sides
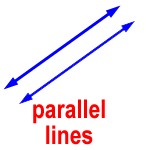
parallel lines – two lines in the same plane that are the same distance apart at all points and never meet
parallelogram – a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides

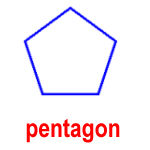
pentagon – a polygon with five sides
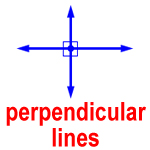
perpendicular lines – two lines that meet to form four right angles
plane – a flat surface that extends in all directions without end

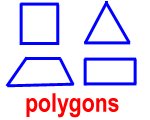
polygon – a closed plane figure made of connected line segments
Triangles, squares, and rectangles are examples of polygons. They are all closed shapes.
quadrilateral – a polygon with four sides

R-V
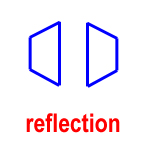
reflection – a flip; a way of moving a shape across a line, producing a mirror image, like flipping a pancake
regular polygon – a polygon with all congruent sides and all equal angles
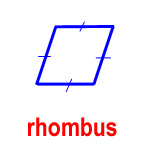
rhombus – a parallelogram with four congruent sides
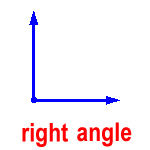
right angle – an angle that is exactly 90°
A right angle makes a perfectly square corner.
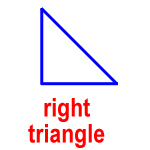
right triangle – a triangle with one right angle
rotation – a turn; turning or spinning a shape, like a doing a cartwheel
rotational symmetry – when a figure is turned 180° or less and produces a figure that is identical

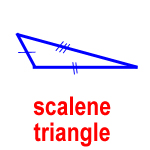
scalene triangle – a triangle with no congruent sides
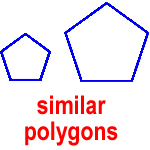
similar polygons – polygons that have the same shape but different sizes
straight angle – an angle that is exactly 180°
A straight angle makes a perfectly straight line.

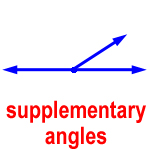
supplementary angles – two angles that have a sum of 180°
transformation – a movement of a shape on a plane; a change in a shape; a way of mapping the shape onto another space
Examples of transformations are translations, reflections, and rotations.
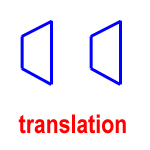
translation – a slide; moving a shape along a line or scooting it over
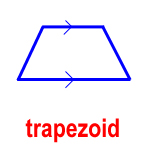
trapezoid – a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides
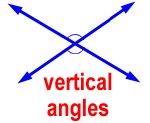
vertical angles – the opposite angles formed when two lines cross
Vertical angles are always congruent angles. They have the same measurement.
Practice
1. Match the type of angle with its picture.
Check the box or boxes that describe each set of angles. There may be more than one correct answer.
6. What are two lines that never meet called?
A) plane
B) intersecting
C) perpendicular
D) parallel
7. What are two lines that meet to form four right angles called?
A) parallel
B) corresponding
C) perpendicular
D) congruent
8. What is a flat surface that extends with no end?
A) plane
B) parallel
C) perpendicular
D) congruent
9. Which two angles are corresponding?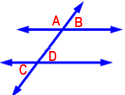
A) B and D
B) A and B
C) B and C
D) C and D
10. Which two angles are vertical?
A) A and B
B) B and D
C) C and D
D) B and C
11. Which two angles are supplementary?
A) C and D
B) A and B
C) B and D
D) B and C
Match the polygon with its name.
25. These two polygons are ___.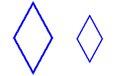
A) regular
B) similar
C) congruent
26. These two polygons are ___.
A) regular
B) similar
C) congruent
27. These two polygons are ___.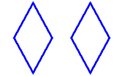
A) regular
B) similar
C) congruent
28. The transformation shown here is a ___.
A) translation
B) reflection
C) rotation
29. The transformation shown here is a ___.
A) translation
B) reflection
C) rotation
30. The transformation shown here is a ___.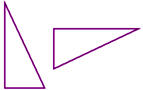
A) translation
B) reflection
C) rotation
31. What is the angle of rotation in this rotation?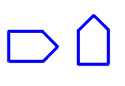
A) 90° counter-clockwise
B) 90° clockwise
C) 180°
32. What is the angle of rotation in this rotation?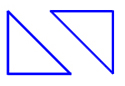
A) 90° counter-clockwise
B) 90° clockwise
C) 180°
33. What is the angle of rotation in this rotation?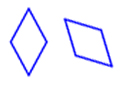
A) 45° counter-clockwise
B) 45° clockwise
C) 90° counter-clockwise
D) 90° clockwise
34. Does this figure have line symmetry?
35. Does this figure have line symmetry?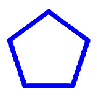
36. Does this figure have line symmetry?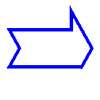
37. Does this figure have line symmetry?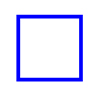
38. Does this figure have rotational symmetry?
39. Does this figure have rotational symmetry?
40. Does this figure have rotational symmetry?
41. Does this figure have rotational symmetry?