Published by K12 Handhelds, Inc.
Long Beach, CA
www.k12handhelds.com
Phone: 800-679-2226
Copyright © 2005 by K12 Handhelds, Inc. License CC-by, 
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 United States License.
Developed in conjunction with Wicomico County Schools.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Polygons
- Triangle
- Quadrilateral
- Square
- Rectangle
- Parallelogram
- Rhombus
- Trapezoid
- Pentagon
- Hexagon
- Octagon
- Transformations
- Three-Dimensional Figures
- Cube
- Sphere
- Cylinder
- Cone
- Pyramid
- Prism
- Glossary
Introduction
Geometry is a kind of math that studies the relationships between lines, shapes, and three-dimensional figures. Geometry is important to many jobs. Builders use geometry to figure out how much lumber and other material they need. Scientists use geometry to calculate formulas. People use geometry to figure out how much fencing to buy or how much paint they need to paint a room.
Polygons
A polygon is a closed figure or shape with straight sides. Examples of polygons are squares and triangles. A circle is not a polygon because it has no straight sides.
Here are several types of polygons:
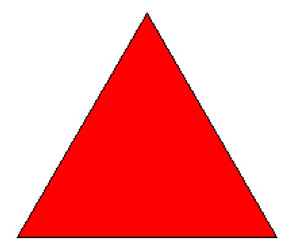
Triangle
A triangle has three sides.
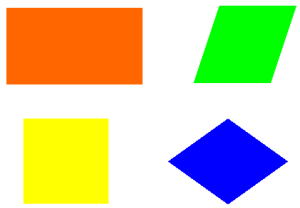
Quadrilateral
A quadrilateral has four sides.
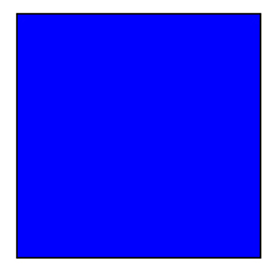
Square
A square is a quadrilateral that has four right angles and four sides that are all the same length.
Rectangle
A rectangle is a quadrilateral that has four right angles and opposite sides that are parallel.

Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides that are parallel and the same length.
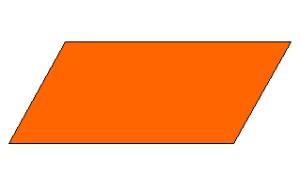
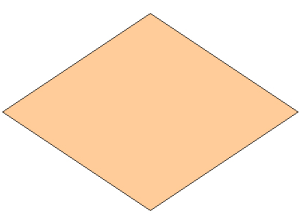
Rhombus
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with four sides that are the same length.
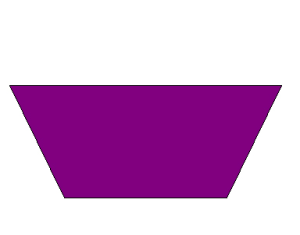
Trapezoid
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with only two sides that are parallel.
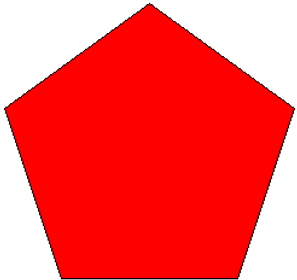
Pentagon
A pentagon is a polygon with five sides.
Hexagon
A hexagon is a polygon with six sides.
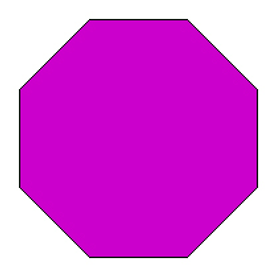
Octagon
An octagon is a polygon with eight sides.
Perimeter is the distance around the outside of a shape. Adding the length of each side of a polygon will give you the perimeter. People often need to know the perimeter of something. For example, if you are going to buy fencing to go around your yard, you will need to know the perimeter.
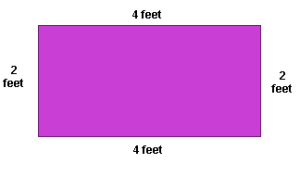
The perimeter of this rectangle is 12 feet. You can see this by adding the length of all the sides.
Perimeter = 4 feet + 2 feet + 4 feet + 2 feet
BONUS: The formula for calculating the perimeter of a rectangle is:
Perimeter = (2 x base)) + (2 x height)
The area of a shape is the amount of space inside of shape. Because area measures the space inside, it is measured in square units of measure, such as square inches or square miles. If you need to know how much carpet to buy for a room, you will need to calculate the area.
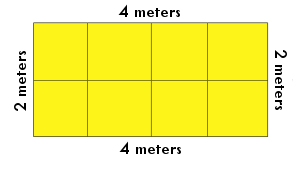
BONUS: The formula for calculating the area of a quadrilateral is:
Area = base x height
Transformations
A transformation is a change in a shape, or a way of mapping the shape onto another space. Examples of transformations are slides, flips, and turns.
A slide, or translation, is moving a shape along a line. The shape is scooted over, like you’d slide a plate from one person to another. Here is an example of a slide:
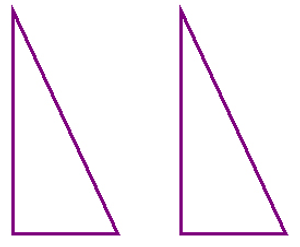
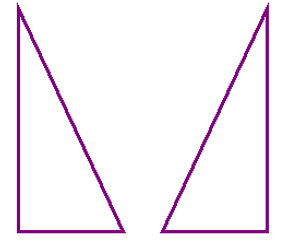
A flip, or reflection, is a way of moving a shape across a line, producing a mirror image. It is like flipping a pancake. Here is an example of a flip:
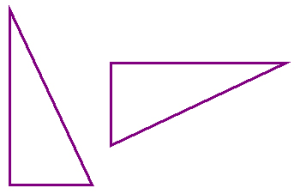
A turn, or rotation, is the turning or spinning a shape. It is like a person doing a cartwheel. Here is an example of a turn:
Shapes that are congruent have the same shape and size. They could be slid, flipped, or turned and would then be exactly the same. These are examples of congruent shapes:

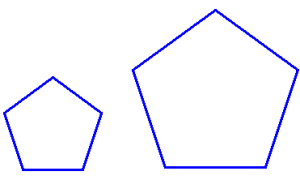
Shapes that are similar have the same shape, but may be different sizes. These are examples of similar shapes:
Some shapes can be tessellated. A tessellation of a shape is when the shape is repeated so that it covers a surface completely without leaving any space. Here is an example of a tessellation:
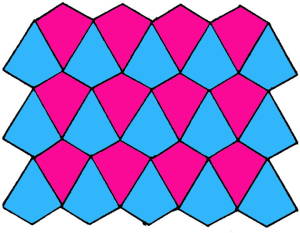
You can use the Tessellation program on your handheld to create your own tessellations.
Three-Dimensional Figures
Three-dimensional figures are figures in space that have length, width, and depth. They are solid objects like a cube, a sphere, or a pyramid. Sometimes three-dimensional is abbreviated as 3D. 3D movies are called that because objects on the screen seem to jump out like three-dimensional figures.
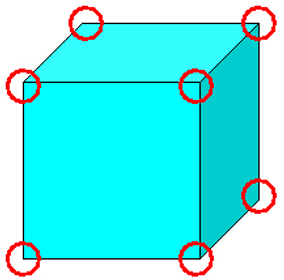
The sides of a three-dimensional figure are its flat surfaces. The edges are where the faces meet. The vertices are the corners or points where three or more surfaces meet.
Here are several types of three-dimensional figures:
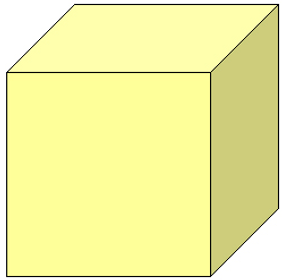
Cube
A cube is a three-dimensional figure with six identical square faces. All the sides of a cube are equal. All the faces are squares. Examples of a cube include dice and a block.
Sphere
A sphere is a round three-dimensional figure. Examples of a sphere include a ball and the earth.

Cylinder
A cylinder is a three-dimensional figure with two flat circular faces. Examples of cylinders include a log and a drum.

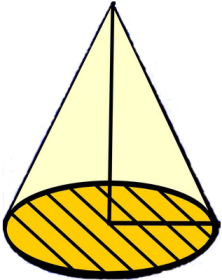
Cone
A cone is a three-dimensional figure with a circular flat base and another curved surface that goes up to a point. An example of a cone is an ice cream cone.
Pyramid
A pyramid is a three-dimensional figure with a flat polygon base and triangular surfaces that go up to a point. The ancient Egyptians built the famous stone pyramids in Egypt.

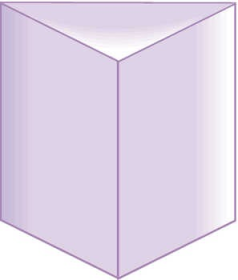
Prism
A prism is a three-dimensional figure with two faces that are parallel polygons and other faces that are parallelograms. A rectangular prism has two parallel rectangles. A triangular prism has two parallel triangles. An example of a rectangular prism is a box of cereal. The kind of glass prism you might use in science to bend light is a triangular prism.
The volume of a three-dimensional figure is the amount of cubic space inside the shape. Because volume measures the space inside, it is measured in cubic units of measure, such as cubic inches or gallons. If you need to know how much water will be needed to fill a swimming pool, you will need to calculate the volume.
BONUS: The formula for calculating the volume of a rectangular prism is:
Volume = length X width X depth
Glossary
area – the amount of space within a closed shape; the number of square units needed to cover a figure
base – the flat face on which a 3 dimensional figure can rest.
closed figure – a figure that starts and ends at the same point and has no open gaps
cone – a three-dimensional figure with a circular flat base and another curved surface that goes up to a point

congruent – having the same shape and same size
cube – a three-dimensional figure with six identical square faces
cylinder – a three-dimensional figure with two flat circular faces
edge – a line segment where two faces of a 3-dimensional figure meet.
face – a flat side of a three-dimensional figure
geometry – a field of math that studies the relationships between lines, shapes, and three-dimensional figures
hexagon – a polygon with six sides
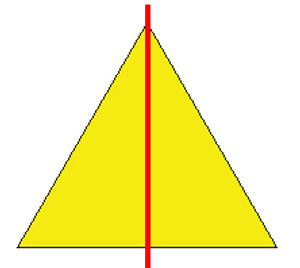
line of symmetry – a line on which a figure can be folded so that both sides are the same
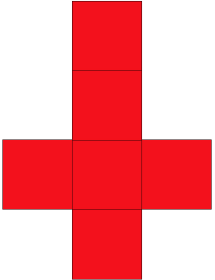
net – a flat pattern that can be folded to make a three-dimensional figure
octagon – a polygon with eight sides
open figure – a figure that does not start and end at the same point.
parallel – lines that are exactly the same distance apart and would never meet

parallelogram – a quadrilateral with opposite sides that are parallel and the same length
pentagon – a polygon with five sides
perimeter – the distance around the outside of an object or shape
polygon – a closed figure with straight sides
pyramid – a three-dimensional figure with a flat polygon base and triangular surfaces that go up to a point

quadrilateral – a polygon with four sides
rectangle – a quadrilateral that has four right angles and opposite sides that are parallel
rectangular prism – a three-dimensional figure with two faces that are parallel rectangles and other faces that /g are also rectangles
reflection – flip; a movement of a figure across a line, producing a mirror image
rhombus – a quadrilateral with four sides that are the same length
right angle – an angle that is 90 degrees

rotation – turn; the turning of a figure
side – a line that is a part of a polygon
similar – having the same shape, but possibly a different size
sphere – round three-dimensional figure; a ball
square – a quadrilateral that has four right angles and four sides that are all the same length
tessellation – repeated shapes that cover a flat surface without overlapping or leaving any gaps
three-dimensional figure – a figure in space that has length, width, and depth; it is a solid object
transformation – a change in a shape, or a way to mapping the shape onto another space; examples: translation, reflection, rotation
translation – slide; to move a figure along a line
trapezoid – a quadrilateral with only two sides that are parallel
triangle – a polygon with three sides
two-dimensional figure – a closed figure that has length and width; a flat object
vertex – the common point of three or more edges of a three-dimensional figure; plural form is vertices
volume – the amount of 3dimensional space occupied by an object